MULTIMEDIA
TV debut
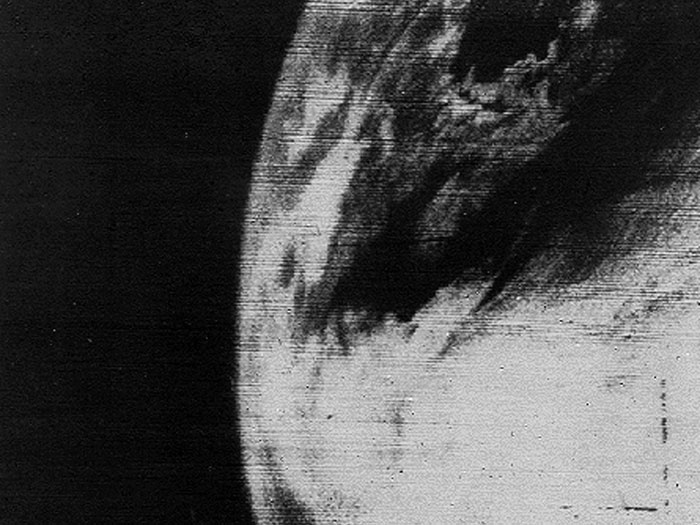
The first television picture of Earth from space. Image taken by TIROS 1 on April 1, 1960.
Credit
Image and caption courtesy of NASA Goddard Photo and Video photostream. Credit: NASA.

The first television picture of Earth from space. Image taken by TIROS 1 on April 1, 1960.
Image and caption courtesy of NASA Goddard Photo and Video photostream. Credit: NASA.
