General questions
-
What’s the difference between climate change and global warming?
“Global warming” refers to the long-term warming of the planet. “Climate change” encompasses global warming, but refers to the broader range of changes that are happening to our planet, including rising sea levels; shrinking mountain glaciers; accelerating ice melt in Greenland, Antarctica and the Arctic; and shifts in flower/plant blooming times.
detailed answer -
What’s the difference between weather and climate?
“Weather” refers to the more local changes in the climate we see around us, on short timescales from minutes to hours, to days to weeks. Examples are familiar – rain, snow, clouds, winds, thunderstorms, sleet, and hail.
“Climate” refers to longer-term averages (which may be regional or global) and can be thought of as the weather averaged over several decades.
detailed answer -
Is it too late to prevent climate change?
Humans have caused major climate changes to happen already, and we have set in motion more changes still. However, if we stopped emitting greenhouse gases today, the rise in global temperatures would begin to flatten within a few years. Temperatures would then plateau but remain well-elevated for many, many centuries.
detailed answer -
Do scientists agree on climate change?
Yes, the vast majority of actively publishing climate scientists – 97 percent – agree that humans are causing global warming and climate change.
detailed answer -
What is NASA's role in climate research?
NASA’s role is to make observations of our Earth's systems (geosphere, biosphere, cryosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere)--and how they connect--that can be used by the public, researchers, policymakers and to support strategic decision-making. The core responsibility of NASA is to conduct rigorous scientific research. It's important to clarify that NASA does not advocate for specific climate policies.
detailed answer
Climate data
-
What types of data do scientists use to study climate?
Climate researchers employ a wide range of direct and indirect measurements to thoroughly investigate Earth's climate history. These measurements include data from natural sources like tree rings, ice cores, corals, and sediments from oceans and lakes. Additionally, data from satellites in space, instruments on the International Space Station, aircraft, ships, buoys, and ground-based instruments are all vital for this research. This comprehensive array of data sources allows scientists to gain a detailed understanding of Earth's climate history.
detailed answer -
How do scientists measure global temperature?
Modern weather observations primarily originate from a network of sources, including weather stations, weather balloons, radar systems, ships, buoys, and satellites.
detailed answer -
Can scientists use global temperature data as is?
No. The Goddard Institute for Space Studies (GISS) utilizes temperature data for conducting long-term climate studies. To ensure the reliability of station data for such research, it's crucial that the time series of observations are consistent. We need to eliminate any temperature fluctuations that are not caused by climate-related factors. These fluctuations can occur due to station relocations, equipment upgrades, or the merging of data from various sources into a single dataset.
detailed answer -
Once the invalid data are eliminated, are global temperature data ready to use?
Not yet. In order to use temperature data effectively, we have to make adjustments to account for all the changes that have occurred over the past 100-150 years.
detailed answer -
How do scientists deal with changes in where data come from?
Major climate research organizations worldwide have developed mathematically rigorous, peer-reviewed data-processing methods to identify and compensate for changes in observing conditions.
detailed answer -
How do scientists know their data-processing techniques are reliable?
The global temperature records calculated by U.S. and other countries are remarkably similar, even though they use different methods to process the data. NASA's Goddard Institute for Space Studies (GISS), National Climatic Data Center (NCDC), and other respected groups subject their techniques and processed data to extensive peer-reviewed analyses.
detailed answer -
Does data processing make temperature data warmer?
Almost half of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's (NOAA) corrected data are cooler than the original records. NOAA's corrections of temperatures over the oceans — done to compensate for changes in methods of observing the temperature of water at the surface of the ocean — reduced the warming trend in global temperature.
detailed answer -
Does data processing destroy the original data?
No, the original records are preserved and are available at no cost online. You can access the National Climatic Data Center's (NCDC) U.S. and global records here.
detailed answer
Greenhouse gases
-
What is the greenhouse effect?
The greenhouse effect is the process through which heat is trapped near Earth's surface by substances known as 'greenhouse gases.' Imagine these gases as a cozy blanket enveloping our planet, helping to maintain a warmer temperature than it would have otherwise. Greenhouse gases consist of carbon dioxide, methane, ozone, nitrous oxide, chlorofluorocarbons, and water vapor. Water vapor, which reacts to temperature changes, is referred to as a 'feedback', because it amplifies the effect of forces that initially caused the warming.
detailed answer -
How might Earth’s atmosphere, land, and ocean systems respond to changes in carbon dioxide over time?
The amount of anthropogenic carbon dioxide (CO2) absorbed by Earth's life forms, ocean, and other "sinks" might decrease as time goes by. Natural carbon sinks (the carbon absorbers, as opposed to "sources," which release carbon) on land and in the ocean have become less effective over time. That is, natural sinks that removed about 60% of annual human-caused CO2 emissions in 1959 now remove about 55% today.
detailed answer -
Which is a bigger methane source: cow belching or cow flatulence?
Contrary to common belief, it's actually cow belching caused by a process called enteric fermentation that contributes to methane emissions.
detailed answer -
Can new NASA carbon-to-oxygen conversion technology like MOXIE be used to address climate change?
Since MOXIE works by ingesting carbon dioxide – the gas that’s mostly driving climate change here on Earth – and produces oxygen, a lot of people wondered whether it could it be helpful on our own planet. But while technology is part of any plan for addressing climate change, the conversion that MOXIE accomplished on Mars is not a viable approach.
detailed answer
Global temperatures (land and ocean)
-
Why does the temperature record shown on your "Vital Signs" page begin at 1880?
Three of the world’s most complete temperature tracking records, maintained by NASA’s Goddard Institute for Space Studies, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s National Climactic Data Center and the UK Meteorological Office’s Hadley Centre, begin in 1880. The oldest continuous temperature record is the Central England Temperature Data Series, which began in 1659, and the Hadley Centre has some measurements beginning in 1850, but there are too few data before 1880 for scientists to estimate average temperatures for the entire planet.
detailed answer -
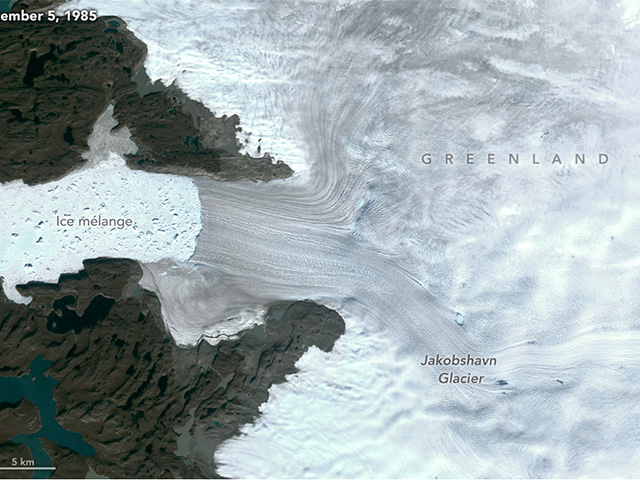
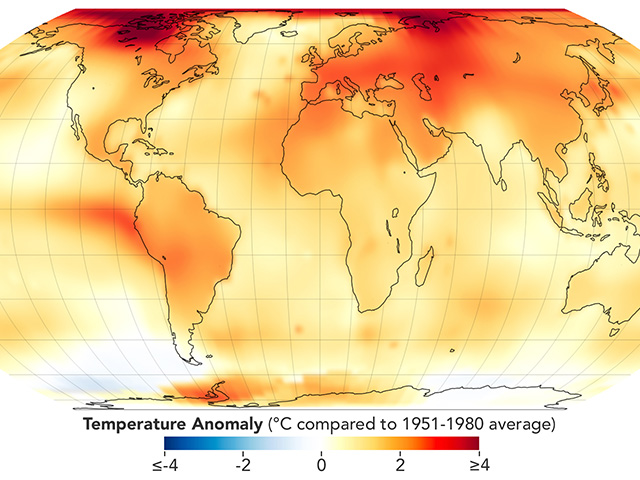
Has Earth continued to warm since 1998?
Yes, evidence shows warming from 1998 to the present, with 2014, 2015, 2016, 2017, 2018, 2019, and 2020 being the hottest years globally since 1880.
detailed answer -
Which measurement is more accurate: taking Earth’s surface temperature from the ground or from space?
Satellites technically do not measure either temperature or the surface (where people live). Therefore, it's safe to say that ground thermometers are more accurate than satellite measurements.
detailed answer -
Is the ocean continuing to warm?
Yes, the ocean is continuing to warm. Notably, all ocean basins have been experiencing significant warming since 1998, with more heat being transferred deeper into the ocean since 1990.
detailed answer -
Can you explain the urban heat island effect?
While urban areas are warmer than surrounding rural areas, the urban heat island effect has had little to no impact on our warming world because scientists have accounted for it in their measurements.
detailed answer
Ice and snow
-
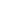
Are the land-based ice sheets in Greenland and Antarctica continuing to lose mass (ice)?
Data from NASA's GRACE satellites, which measured Earth’s gravity field, show that the land ice sheets in both Antarctica and Greenland have been losing mass (ice) since 2002.
detailed answer -
How are Earth’s mountain glaciers faring in a warming world?
On average, most of Earth’s mountain glaciers are continuing to melt.
detailed answer -
How is Earth’s sea ice faring in our warming world?
Arctic sea ice volume and extent have been declining since record-keeping began in the late 1970s and prior. Antarctic sea ice extent is currently below the long-term average of prior decades since 1979.
detailed answer -
What’s the difference between glacier or ice sheet surface mass balance and total mass balance?
Surface mass balance is the difference between the precipitation (rain and snow) that has accumulated on the upper surfaces of glaciers and ice sheets and what has been lost due to melt, eventual runoff, and evaporation.
Total mass balance is the difference between total mass gains and total mass losses, which includes ice lost in the lower margins due to calving and thinning from contact with warm ocean waters.
detailed answer -
If all of Earth's ice melts and flows into the ocean, what would happen to the planet's rotation?
Melting land ice, like mountain glaciers and the Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets, will change Earth’s rotation only if the meltwater flows into the ocean. For example, if the Greenland ice sheet were to completely melt and the meltwater were to completely flow into the ocean, then global sea level would rise by about seven meters (23 feet) and Earth would rotate more slowly, with the length of the day becoming longer than it is today, by about 2 milliseconds.
Melting sea ice, such as the Arctic ice cap, does not change sea level because the ice displaces its volume and, hence, does not change Earth’s rotation.
detailed answer
The sun, volcanoes, and more
-
Is the Sun causing global warming?
No. The Sun can influence Earth’s climate, but it isn’t responsible for the warming trend we’ve seen in recent decades.
detailed answer -
What happens if the next solar cycle becomes less active? Will we enter into a new ice age?
No. Even if the amount of radiation coming from the Sun were to decrease as it has before, it would not significantly affect the global warming coming from long-lived, human-emitted greenhouse gases. Further, given our greenhouse gas emissions to date and those expected to come, the evidence points to the next “ice age” being averted altogether.
detailed answer -
What do volcanoes have to do with climate change?
Volcanic eruptions are often discussed in the context of climate change because they release CO2 and other gases into our atmosphere. However, the impact of human activities on the carbon cycle far exceeds that of all the world's volcanoes combined, by more than 100 times.
To put it in perspective, while volcanic eruptions do contribute to an increase in atmospheric CO2, human activities release an amount of CO2 equivalent to what a Mount St. Helens-sized eruption produces every 2.5 hours and a Mount Pinatubo-sized eruption twice daily.
detailed answer -
Is the ozone hole causing climate change?
Yes and no. The ozone hole is not causing global warming, but it is affecting atmospheric circulation.
detailed answer -
The amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is measured at Mauna Loa, Hawaii, by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Could the rising carbon dioxide be caused by the volcano?
The amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the atmosphere is measured by many different methods, all around the world. By using more than one approach, scientists can be sure they’re measuring a global trend, rather than a local variation.
detailed answer -
Do small particles in the air (aerosols) have a warming or cooling effect on the climate?
Both! In general, light-colored particles in the atmosphere will reflect incoming sunlight and cause a cooling effect. Dark-colored particles absorb sunlight and make the atmosphere warmer. Because different types of particles have different effects, aerosols are a hot topic in climate research.
detailed answer
Past climates
-
How do we know what greenhouse gas and temperature levels were in the distant past?
Ice cores are scientists’ best source for historical climate data. Other tools for learning about Earth’s ancient atmosphere include growth rings in trees, which keep a rough record of each growing season’s temperature, moisture and cloudiness going back about 2,000 years. Corals also form growth rings that provide information about temperature and nutrients in the tropical ocean. Other proxies, such as benthic cores, extend our knowledge of past climate back about a billion years.
detailed answer
Other
-
How do I cite your website?
It depends on the style you’re using. Read on for a few examples.
detailed answer -
May I use content and imagery from your website? If so, to whom do I credit them?
Unless otherwise noted, you may use our content and imagery without permission, as long as you provide due credit.
detailed answer