News | June 12, 2014
New NASA space observatory to study carbon conundrums

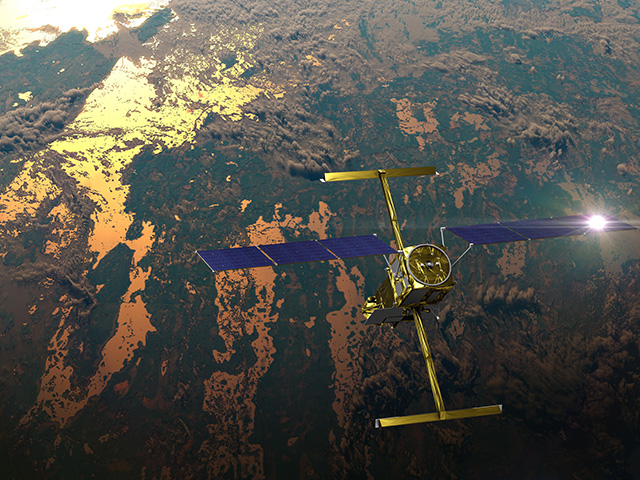
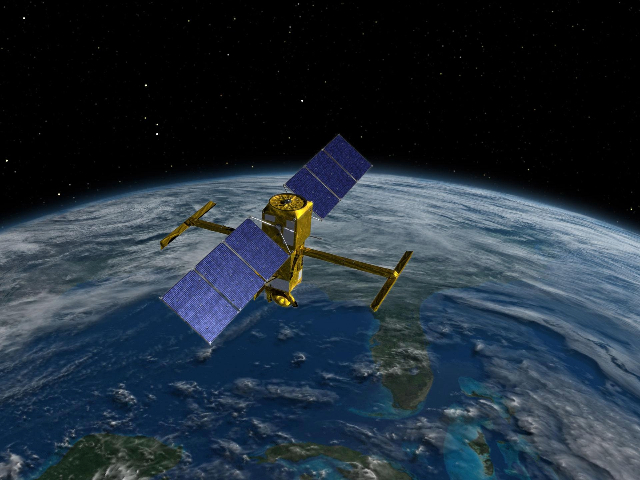
Artist's rendering of NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory (OCO)-2, one of five new NASA Earth science missions set to launch in 2014, and one of three managed by JPL. Credit: NASA-JPL/Caltech
NASA's first spacecraft dedicated to measuring carbon dioxide levels in Earth's atmosphere is in final preparations for a July 1 launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base, California.
The Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) mission will provide a more complete, global picture of the human and natural sources of carbon dioxide, as well as carbon dioxide's "sinks," the natural ocean and land processes by which carbon dioxide is pulled out of Earth's atmosphere and stored. Carbon dioxide, a critical component of Earth's carbon cycle, is the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth's climate.
"Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere plays a critical role in our planet's energy balance and is a key factor in understanding how our climate is changing," said Michael Freilich, director of NASA's Earth Science Division in Washington. "With the OCO-2 mission, NASA will be contributing an important new source of global observations to the scientific challenge of better understanding our Earth and its future."
OCO-2 will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket and maneuver into a 438-mile (705-kilometer) altitude, near-polar orbit. It will become the lead satellite in a constellation of five other international Earth monitoring satellites that circle Earth once every 99 minutes and cross the equator each day near 1:36 p.m. local time, making a wide range of nearly simultaneous Earth observations. OCO-2 is designed to operate for at least two years.
The spacecraft will sample the global geographic distribution of the sources and sinks of carbon dioxide and allow scientists to study their changes over time more completely than can be done with any existing data. Since 2009, Earth scientists have been preparing for OCO-2 by taking advantage of observations from the Japanese GOSAT satellite. OCO-2 replaces a nearly identical NASA spacecraft lost because of a rocket launch mishap in February 2009.
At approximately 400 parts per million, atmospheric carbon dioxide is now at its highest level in at least the past 800,000 years. The burning of fossil fuels and other human activities are currently adding nearly 40 billion tons of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere each year, producing an unprecedented buildup in this greenhouse gas.
Greenhouse gases trap the sun's heat within Earth's atmosphere, warming the planet's surface and helping to maintain habitable temperatures from the poles to the equator. Scientists have concluded increased carbon dioxide from human activities, particularly fossil fuel burning and deforestation, has thrown Earth's natural carbon cycle off balance, increasing global surface temperatures and changing our planet's climate.
Currently, less than half the carbon dioxide emitted into Earth's atmosphere by human activities stays there. Some of the remainder is absorbed by Earth's ocean, but the location and identity of the natural land sinks believed to be absorbing the rest are not well understood. OCO-2 scientists hope to coax these sinks out of hiding and resolve a longstanding scientific puzzle.
"Knowing what parts of Earth are helping remove carbon from our atmosphere will help us understand whether they will keep doing so in the future," said Michael Gunson, OCO-2 project scientist at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California. "Understanding the processes controlling carbon dioxide in our atmosphere will help us predict how fast it will build up in the future. Data from this mission will help scientists reduce uncertainties in forecasts of how much carbon dioxide will be in the atmosphere and improve the accuracy of global climate change predictions."
OCO-2 measurements will be combined with data from ground stations, aircraft and other satellites to help answer questions about the processes that regulate atmospheric carbon dioxide and its role in Earth's climate and carbon cycle. Mission data will also help assess the usefulness of space-based measurements of carbon dioxide for monitoring emissions.
The observatory's science instrument features three high-resolution spectrometers that spread reflected sunlight into its component colors and then precisely measure the intensity of each color. Each spectrometer is optimized to record a different, specific color absorbed by carbon dioxide and oxygen molecules in Earth's atmosphere. The less carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, the more light the spectrometers detect. By analyzing the amount of light, scientists can estimate the relative concentrations of these chemicals.
The new observatory will dramatically increase the number of observations of carbon dioxide, collecting hundreds of thousands of measurements each day when the satellite flies over Earth's sunlit hemisphere. High-precision, detailed, near-global observations are needed to characterize carbon dioxide's distribution because the concentration of carbon dioxide varies by only a few percent throughout the year on regional to continental scales. Scientists will analyze the OCO-2 data, using computer models similar to those used to predict the weather, to locate and understand the sources and sinks of carbon dioxide.